Peanuts (Arachis hypogaea), a widely consumed legume originating from South America, are not just a tasty snack but a treasure trove of nutrients.
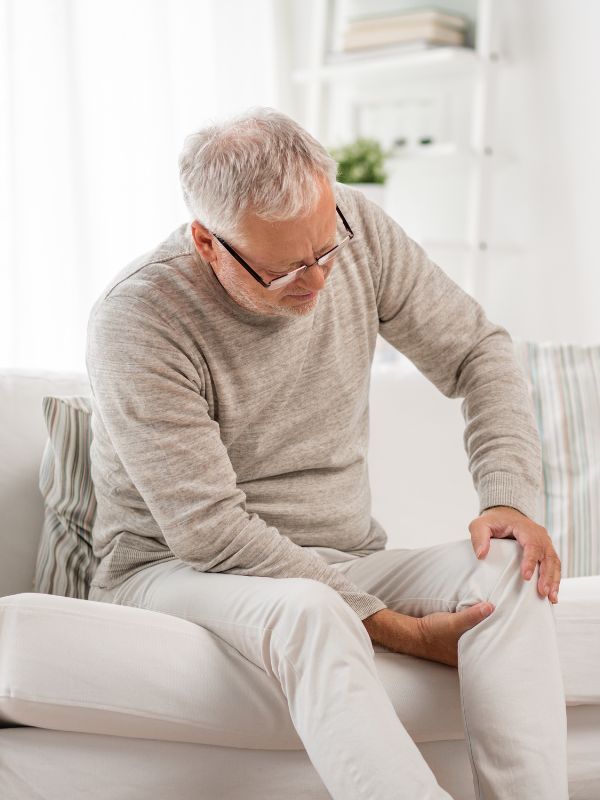
Recent studies reveal their potential as a natural remedy for chronic pain caused by conditions like arthritis, back pain, and osteoporosis.
With their rich profile of unique bioactive compounds, peanuts can help reduce inflammation, improve mobility, and promote overall health.
#1. Reduces Joint Inflammation
Peanuts are rich in polyphenols, specifically p-coumaric acid, which exhibits strong anti-inflammatory effects.
A 2021 study published in Food & Function highlighted that peanut-derived polyphenols help reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukins, both of which contribute to joint pain in arthritis.
Additionally, arginine, an amino acid in peanuts, aids in improving blood flow to inflamed areas, enhancing recovery and pain reduction.

#2. Supports Bone Health
Peanuts contain phytates, which were once thought to interfere with mineral absorption but have now been found to promote bone mineral density when consumed in moderation.
A study in the Journal of Nutrition and Health Sciences (2018) demonstrated that diets including peanuts improved bone health in postmenopausal women, a group particularly prone to osteoporosis.
In addition, zinc in peanuts helps with the repair and regeneration of bone tissue, which is crucial for reducing pain caused by fractures or degenerative conditions.

#3. Improves Circulation to Reduce Pain
Improved circulation is key to managing chronic pain, especially in areas like the back and joints. Peanuts are an excellent source of arginine, which the body converts into nitric oxide.
Nitric oxide is a vasodilator that enhances blood flow to tissues, aiding in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
A clinical trial published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology (2017) found that peanut consumption significantly improved vascular function in participants over six weeks.
#4. Protects Against Chronic Pain Conditions with Resveratrol
Peanuts are one of the richest dietary sources of resveratrol, a compound also found in red wine.
Resveratrol has been shown to reduce chronic inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory enzymes like cyclooxygenase (COX).
A 2020 study in Inflammation Research demonstrated that resveratrol reduced symptoms in patients with osteoarthritis, improving joint flexibility and reducing pain severity.
#5. Promotes Muscle and Tissue Repair
Peanuts provide branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which are critical for muscle repair. These amino acids support the regeneration of tissues around inflamed joints and muscles, reducing discomfort and improving mobility.
A 2022 study published in Nutrients found that peanut-based diets in athletes reduced recovery time after muscle injuries, showing their potential to aid chronic pain sufferers.

#6. Anti-Nociceptive Effects for Pain Management
Peanuts contain bioactive peptides that act as natural painkillers by modulating pain perception pathways.
Research in Frontiers in Pharmacology (2019) found that peanut peptides influenced nociceptive (pain-sensing) neurons, reducing pain signals in patients with inflammatory conditions.
This unique property positions peanuts as more than just a dietary addition but as a natural therapeutic agent.
#7. Aids in Managing Weight to Reduce Joint Stress
Excess weight exacerbates chronic pain, particularly in weight-bearing joints like knees and hips. Peanuts, though calorie-dense, promote satiety due to their high protein and fat content.
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2021) found that regular peanut consumption as part of a balanced diet led to improved weight management without significant calorie excess.
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints, alleviating chronic pain over time.

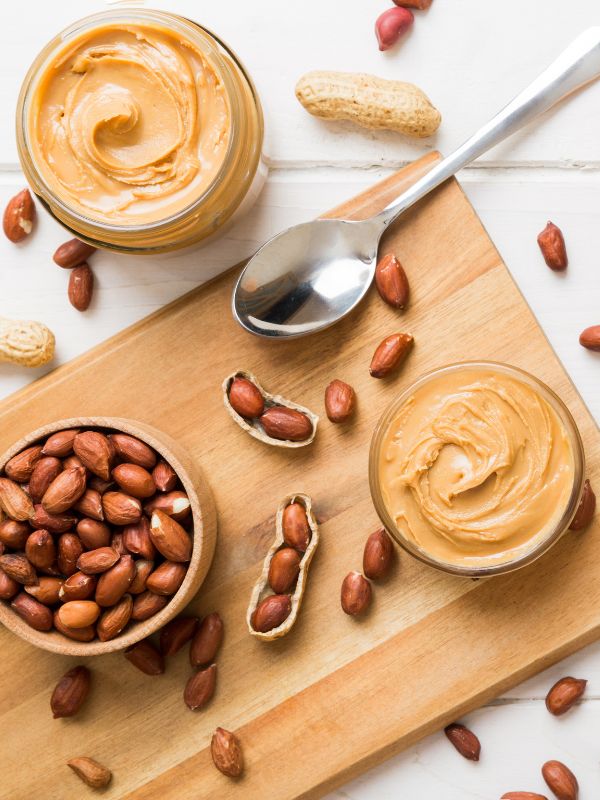
How to Use Peanuts for Pain Relief
Peanut Pain Relief Mixture
Ingredients:
- 1 cup unsalted roasted peanuts.
- 2 tablespoons honey.
- 1 teaspoon grated ginger (anti-inflammatory).
- A pinch of turmeric or cinnamon for added benefits.
Instructions:
- Blend peanuts into a smooth paste.
- Mix in honey, ginger, and spices.
- Store in an airtight container.
Usage:
Consume 1–2 tablespoons daily, preferably in the morning, with warm water or milk.

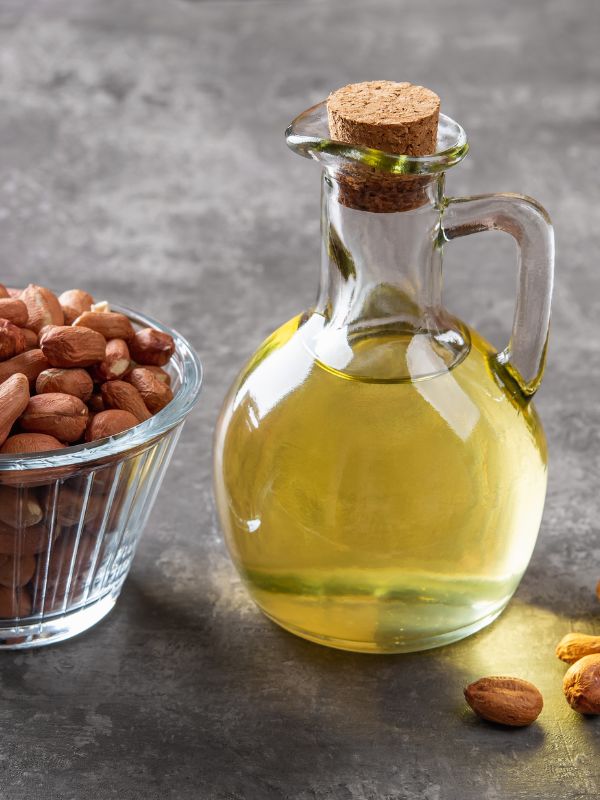
Topical Peanut Oil Massage
Warm peanut oil gently and apply to affected areas, massaging in circular motions to improve circulation and reduce stiffness.

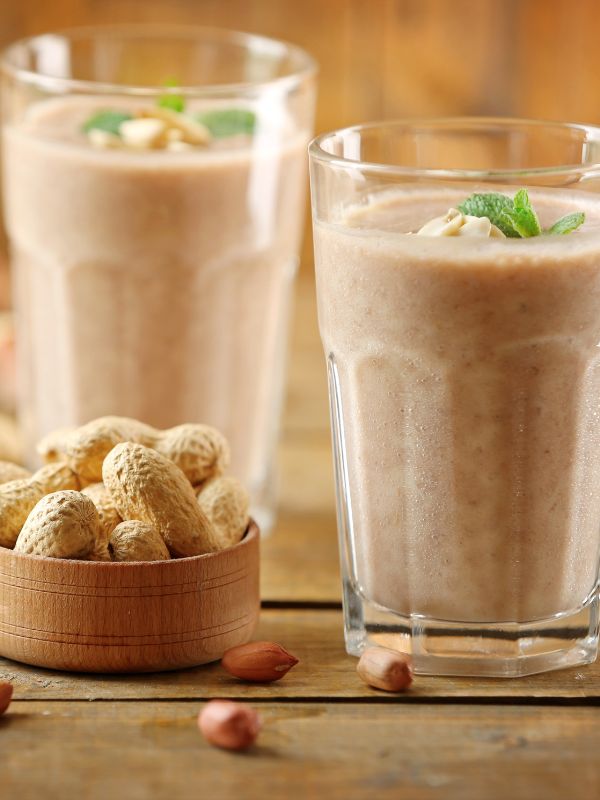
Incorporate Peanuts in Meals
Add roasted peanuts to salads, oatmeal, or stir-fries.
Use peanut butter in smoothies or as a spread on whole-grain toast for a nutritious snack.

Cautions and Precautions
If you have a peanut allergy, avoid peanuts entirely and seek alternatives like almonds or walnuts.
Due to their high-calorie content, limit consumption to 1–2 servings per day to avoid weight gain, which could worsen joint stress.
Peanuts contain moderate levels of purines; individuals with gout should consult their healthcare provider before incorporating peanuts into their diet.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice.
Always consult a healthcare provider before trying new remedies, particularly if you have pre-existing conditions or are on medication.

7 Science-Backed Benefits of Peanuts for Chronic Pain Relief
